

OUR TEACHING & LEARNING APPROACH
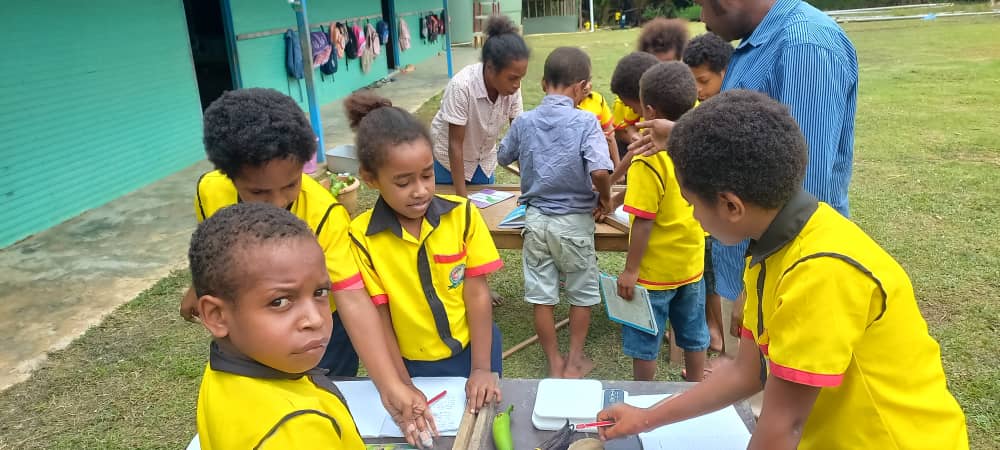


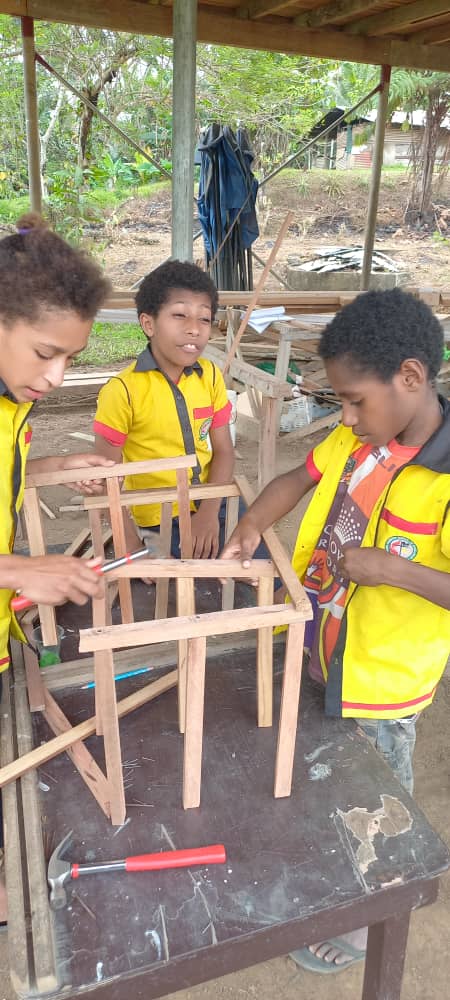
WE ARE FOCUSED ON PROJECT-BASED LEARNING.
We teach hands-on, practical learning experience STEM AIE ( STEM + Arts, Innovation and Entrepreneurship) Programs. Our curriculum is crafted to keep students engaged in design-based problem-solving skills, fostering creativity, leadership and entrepreneurial thinking.


OUR CIRRICULUM SUPPORTS DUAL GRADING SYSTEM.
The unique features of our school is the dual grading system, allowing high performing students to progress faster by skipping grades based on their academic strengths. This flexible approach ensures students learn at their own pace while maximizing their potential.
We integrate innovative teaching strategies bridging the National SBE Curriculum with the Global Learning Standards through the Foundational Literacies, Competencies and Character Qualities to foster 21st Century Skills development.
The ability to read, write, and use English language to communicate and understand the world. It involves not just decoding words but also comprehending and critically analyzing texts.
The ability to understand and use mathematical concepts in everyday life. It includes basic arithmetic, data interpretation, and problem-solving using quantitative information.
The knowledge and understanding of scientific concepts and processes required for personal decision-making, participation in civic and cultural affairs, and economic productivity. It involves the ability to evaluate scientific information and make evidence-based decisions.
The ability to use digital technology, Generative AI, communication tools, online platforms and apps and/or networks to access, manage, integrate, evaluate, and create information in order to function in a knowledge society.
The knowledge, skills, and confidence to make responsible financial decisions. It includes understanding concepts like budgeting, saving, investing, and debt management.
The ability to understand and participate effectively in a diverse society. Cultural literacy involves understanding different cultures and traditions, while civic literacy involves knowing one’s rights and responsibilities as a citizen and participating in the democratic process.
The knowledge, skills, and mindset to identify opportunities, take initiative, and create value. It involves understanding business concepts, financial management, and risk-taking, as well as being innovative and resilient.

Mathematical Modelling in Education
At our school, we explore how knowledge, skills, and personal growth can be represented through mathematical modelling. This process involves creating mathematical representations of real-world scenarios to help us analyze situations, make predictions, and gain valuable insights.
Unlike simply applying formulas, mathematical modelling focuses on building meaningful relationships between variables that reflect real-life patterns and behaviours.
We use various forms of representation, including:
- Graphs (line graphs, bar charts)
- Tables (data comparisons and trends)
- Pie charts (percentage breakdowns)
WHAT IS SYSTEMS THINKING?

Systems Thinking is a holistic approach used to understand how different factors and interactions within a system contribute to possible outcomes.
Comprises software and hardware working together.
Involves mechanical parts and physical components.
Focuses on people and their interactions.
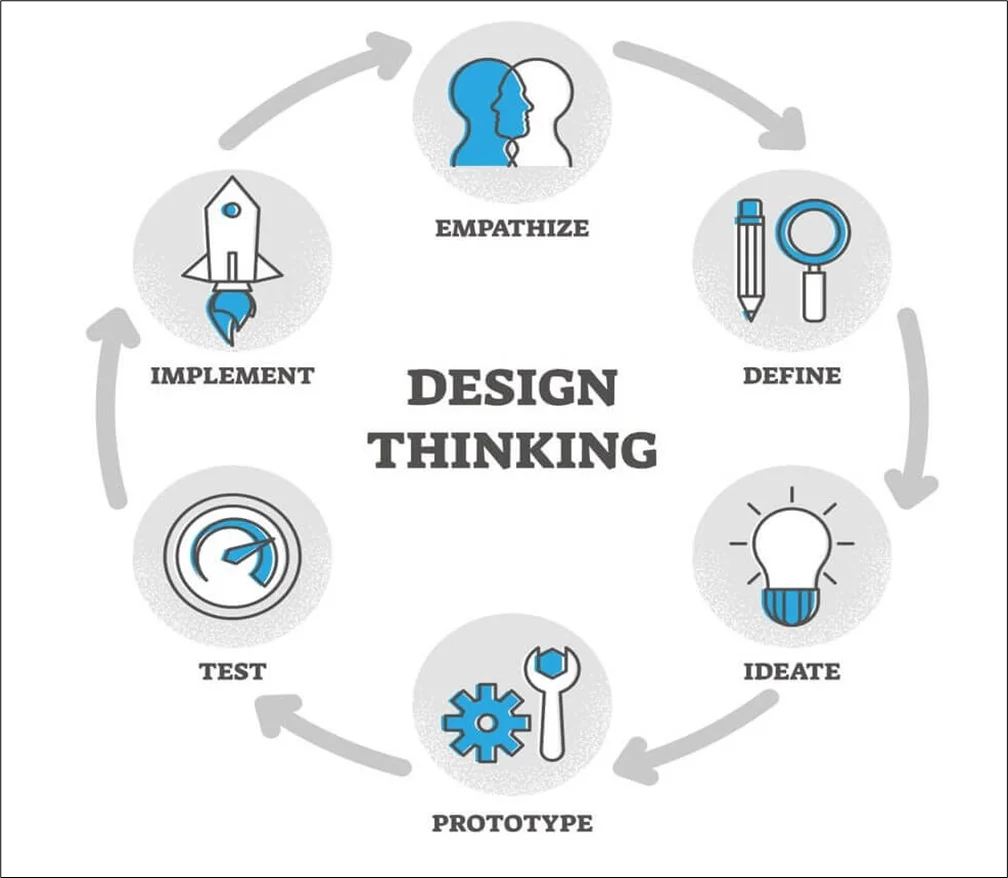
WHAT IS DESIGN THINKING?
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test. Involving five phases—Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test—it is most useful to tackle problems that are ill-defined or unknown.
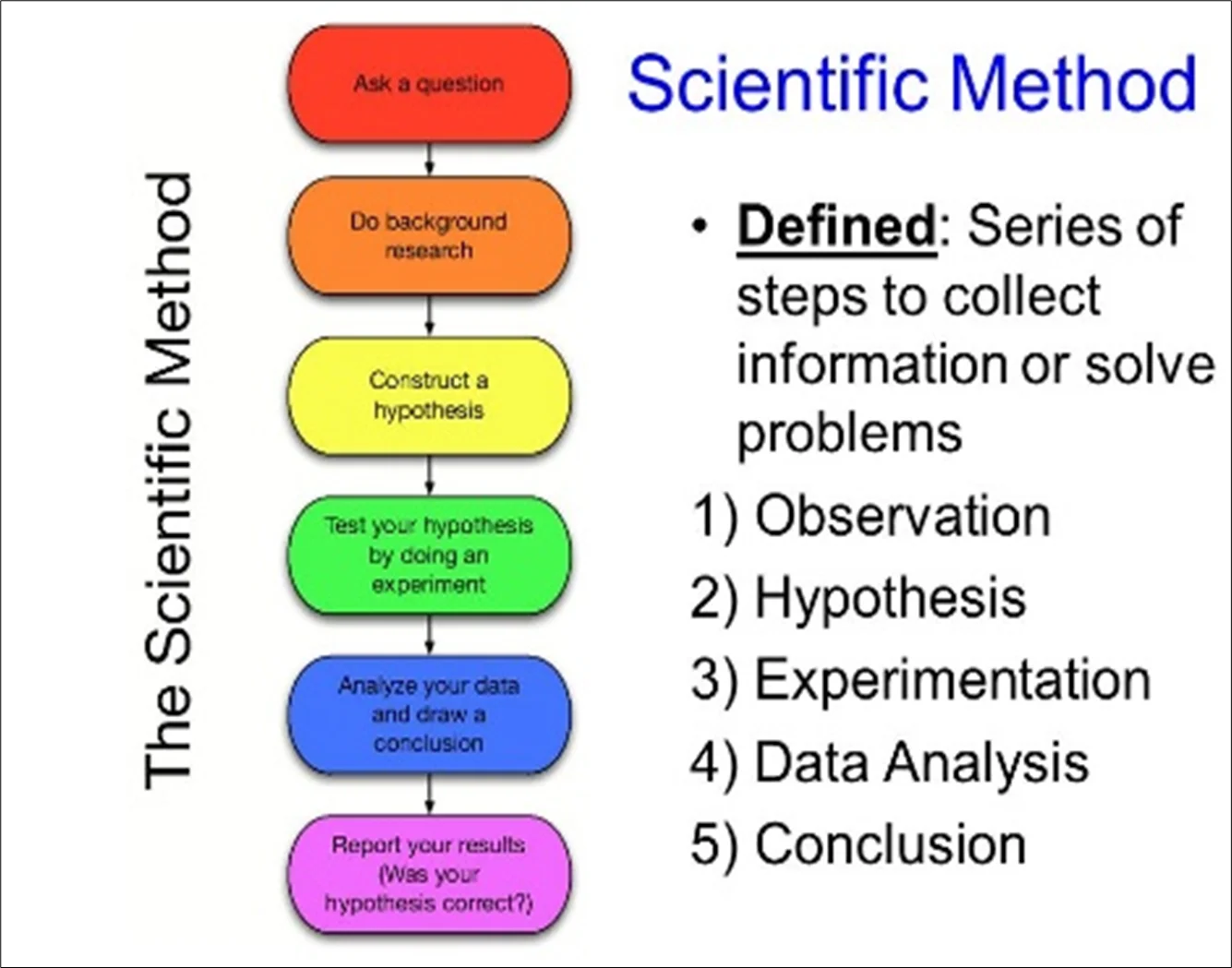
Scientific Enquiry Method
The scientific method is the process of objectively establishing facts through testing and experimentation. It involves making an observation, forming a hypothesis, making a prediction, conducting an experiment, and finally analyzing and presenting the results.
FUTURE OF CONNECTIVITY
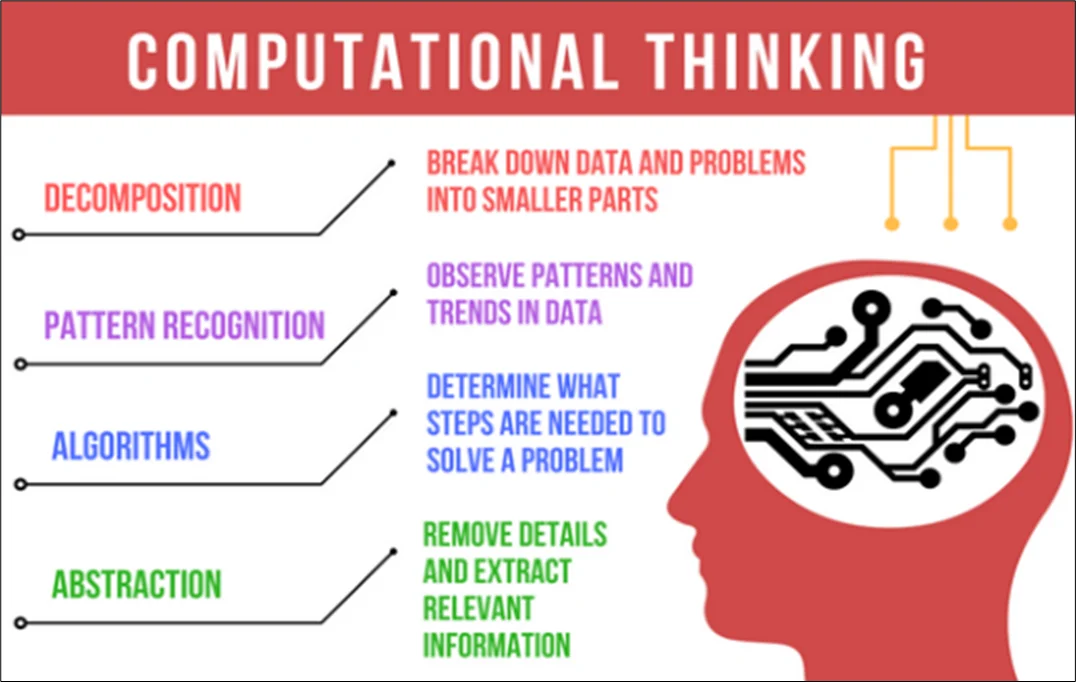
COMPUTATIONAL THINKING
Computational thinking is the mental skill to apply concepts, methods, problem-solving techniques, and logic reasoning, derived from computing and computer science, to solve problems in all areas, including our daily lives





OUR TEACHING & LEARNING STRATEGY:
WE APPLY SYSTEM THINKING IN ALL WAY WE DO!


SOCIAL & CIVIC LITERACY